Plants > Ornamental & Shade Trees > Moringa
Moringa
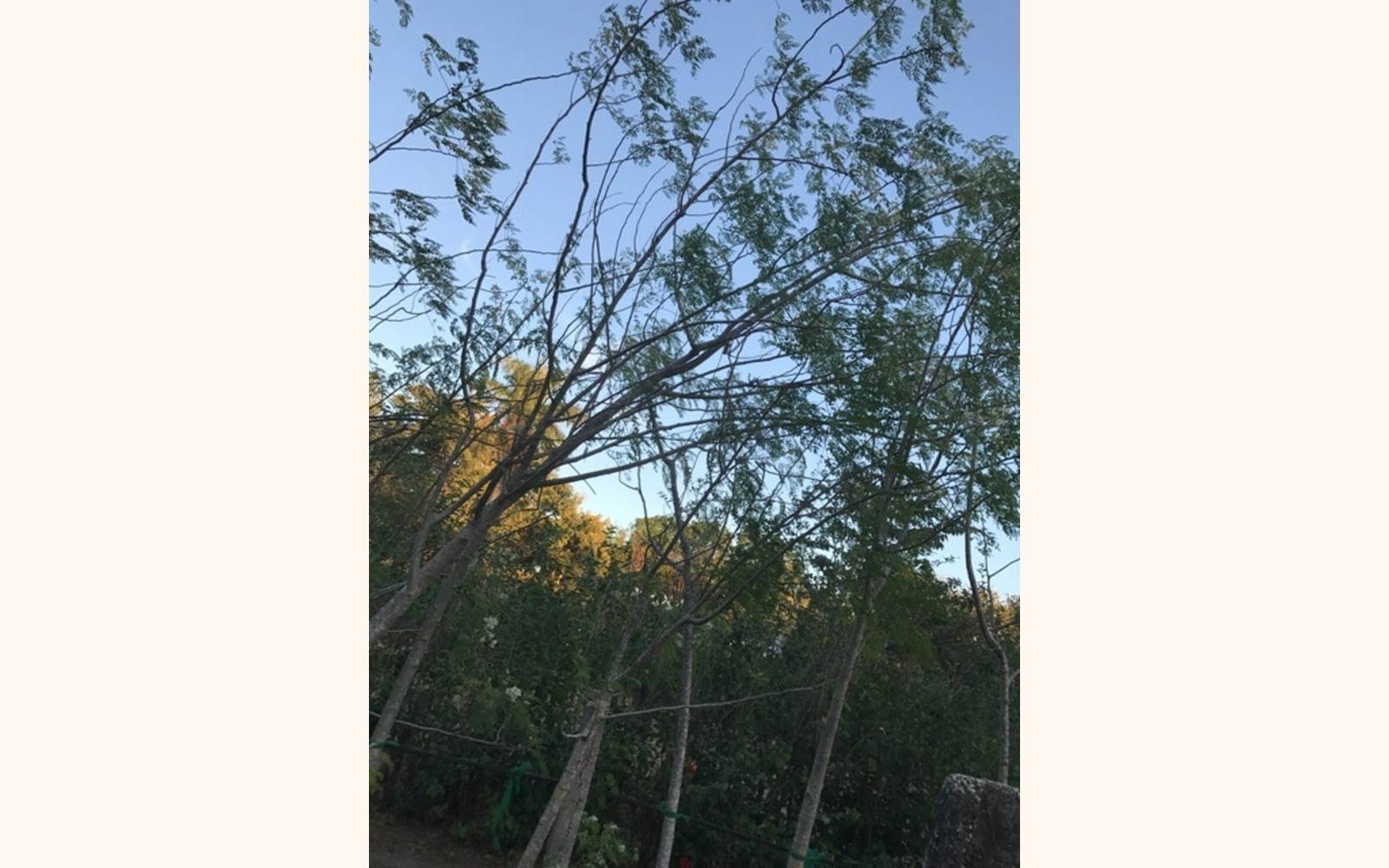
Native to the southern foothills of the Himalayas in northwestern India, this decidouos fast growing tree has been cultivated for its beneficial nutritional value. It has been cultivated for its leaves, pods, and/or its kernels for oil extraction and water purification. The oil has been used as a food supplement, as a base for cosmetics, and for hair and the skin. Many proclaim Miranga's medicinal benefits and along with its strong nutritional benefits; it is often called the Miracle Tree or Tree of Life.
Plant Characteristics
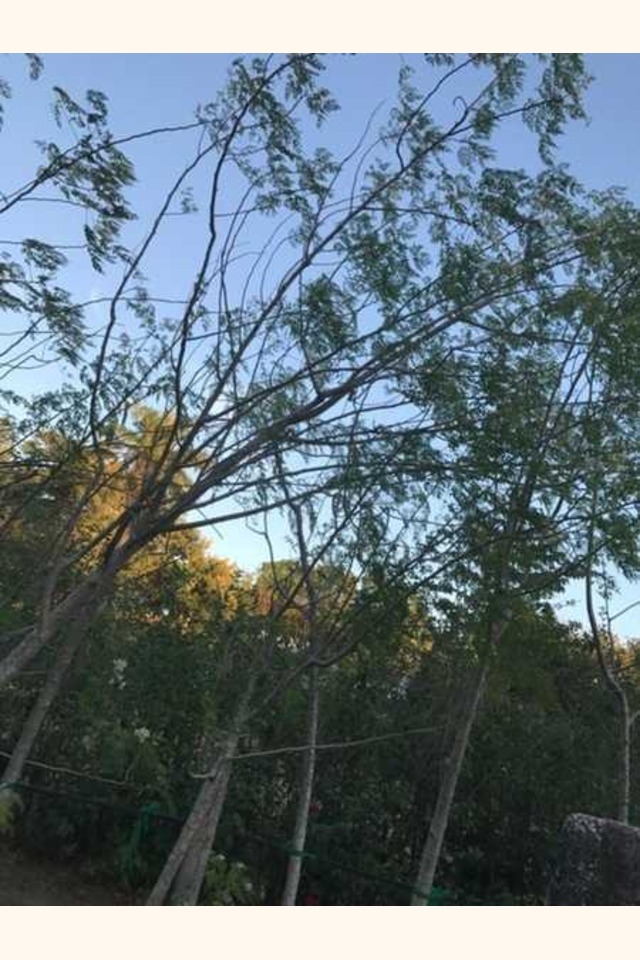
- Height: 10 to 12 M
- Trunk Diameter: 45 CM
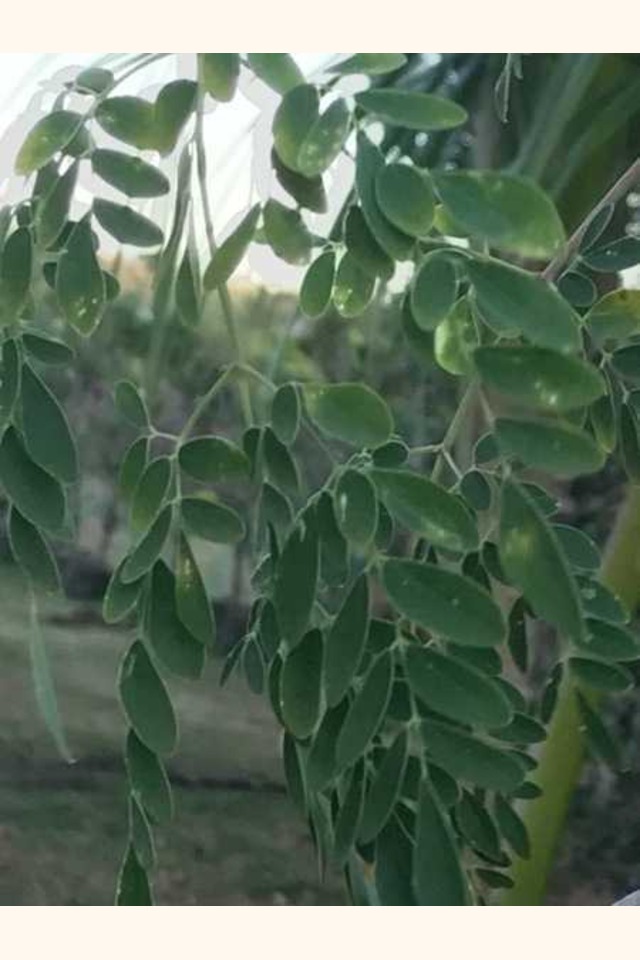
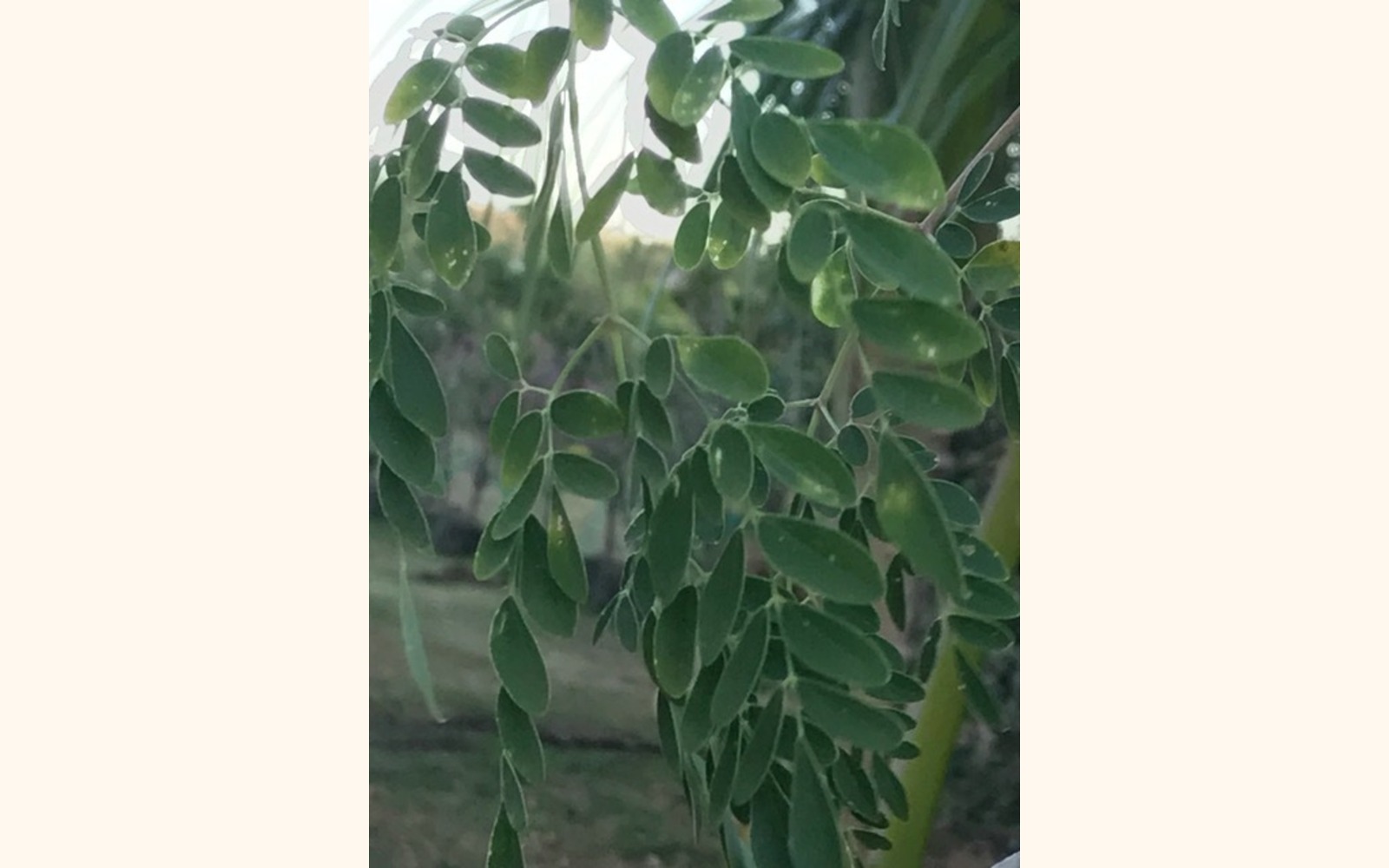
Leaves
"The leaves are small trippanate. They are the most nutritional part of the plant containing "significant source of B vitamins, vitamin C, provitamin A as beta-carotene, vitamin K, manganese, and protein, among other essential nutrients"
Fruit
"The fruit is a hanging, three-sided brown capsule of 20–45 cm size which holds dark brown, globular seeds with a diameter around 1 cm. The seeds have three whitish papery wings and are dispersed by wind and water."
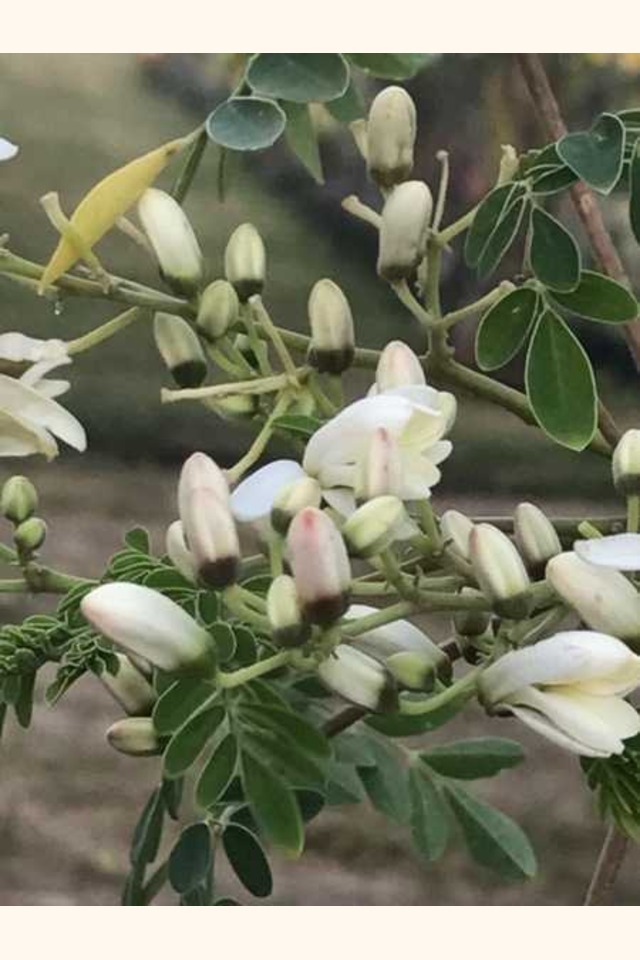
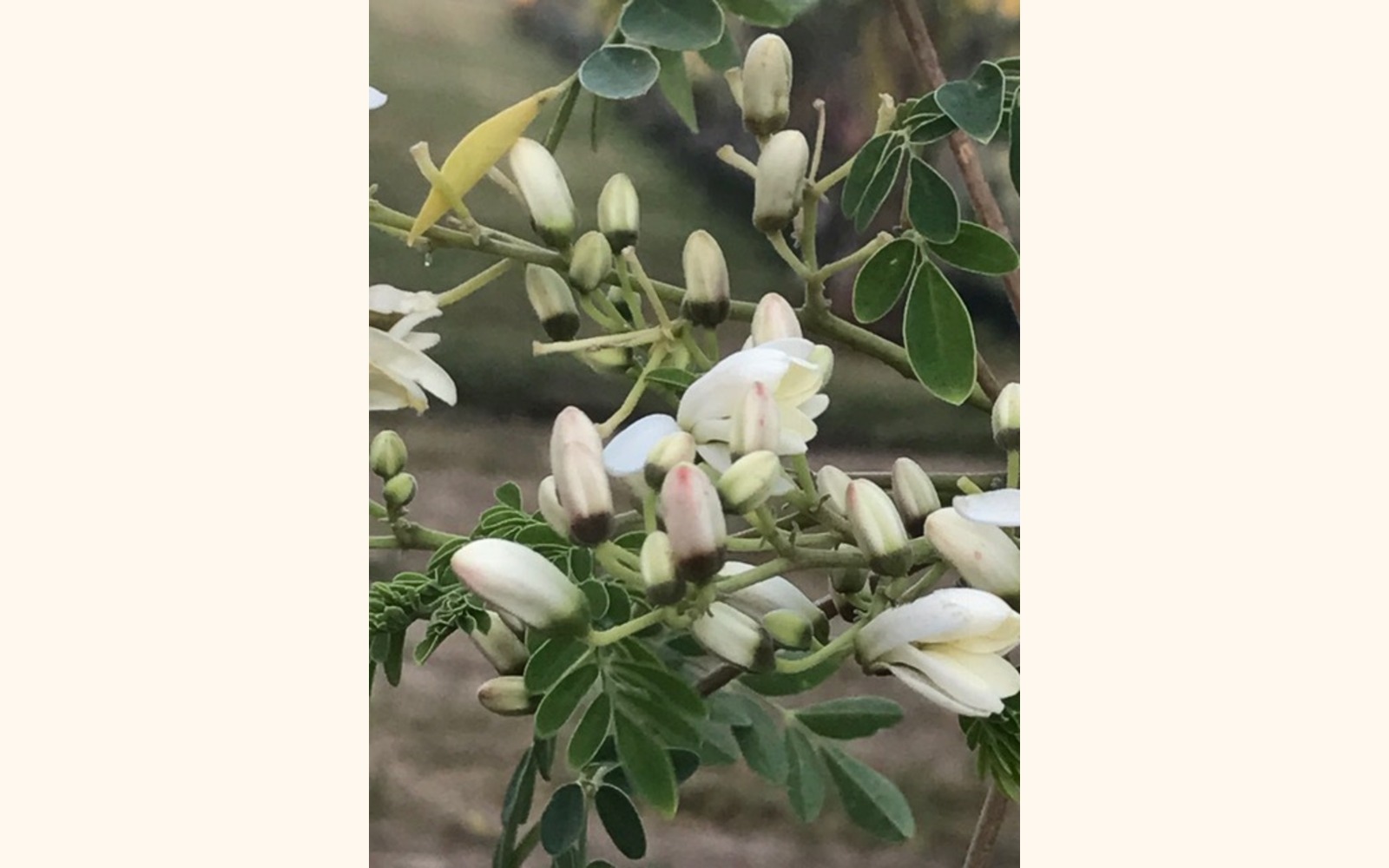
Flowers
"The flowers are fragrant and bisexual, surrounded by five unequal, thinly veined, yellowish-white petals. The flowers are about 1.0-1.5 cm (1/2")long and 2.0 cm (3/4")broad. They grow on slender, hairy stalks in spreading or drooping later flower clusters which have a length of 10–25 cm." They can also be cooked and eaten. Some say they have the flavor of mushrooms.
Bloom Cycle
Flowering usually occurs twice a year and in some places all year round.
Additional Information
Benefits | Desirability
Practically every part of the plant can be used.
Care Instructions
Grows best in sandy or loamy soil.
Natural Associations
This tree has been used for windbreaks, soil erosion, and living fences.
References
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Moringa_oleifera#cite_note-28
Tags
drought tolerant,
Precautions
Moringa can be grown as an annual or perennial plant. In the first year, all pods are edible. Later years also bear inedible bitter pods .